Tags
agriculture, analytic tool, Anna Paseman, Annie Bonebrake, anti-Modernism, Antwerp, art, atlas, Austrian, Bartolomé de las Casas, Bear Flag Revolt, Belgian, Benito Juarez, binding, biography, book, broadsides, California, Cameron Dower, Camille Morgenstern, Carlos Ixta, cartas de poder, cartographer, cartoons, Catholic Church, Chihuahua, Chile, colonization, Communist Party, Dawson's Book Shop, dictionary, documents, Dylan Slavens, Edwin H. Carptenter, encyclopedia, English, European, Fernando Núñez de Guzmán, folletto, forests, France, Francisco de Aefferden, Francisco Laso, French, Gabriel Gonzalez Videla, Galician, Giovanni Paoli, Greek, handmade, heretic, history, Indian, indigenous, iPhone, Isabel Dulfano, Italian, Italy, Jacome Croberger, Jake Tilson, Josep Renau, Juan Pablos, Latin, leather, Leon de Castrón, literary analysis, literature, London, Los Angeles, Madrid, magazines, Manuel Castañares, maps, Marc Jackson, Marisol Padilla Fragosso, marriage, Marriott Library, Mexican Republic, Mexican-American War, Mexico, Mexico City, Miguel Martinez, miner's strike, missions, muralist, news, newspaper, notarization, Olivia Blithell, Pablo Neruda, pamphlet, Pedro Ocharte, persecution, philosophy, photographs, Pierre Laval, poetry, Portuguese, posters, power of attorney, primary sources, printing press, propaganda, protocols, proverbs, Pueblo, Radical Party, Rare Books Department, religion, rivers, saints, Salt Lake City, Shakespeare, signatures, sixteenth century, slave trade, Spanish, Spanish Inquisition, symbols, The University of Utah, theater, torture, Tosh Noskowski, Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, twenty-first century, Urbano Gonzalez Serrano, Utah, Washington, Woolley Dale, WWII

Students from Introduction to Textual Analysis (SPAN3070-1), taught by Prof. Isabel Dulfano, met in the Rare Books Classroom three times Spring Semester 2018 to work with three different sets of books from the rare book collections. Themes were “Narración de cuentos: literatura, historia, viajes, biografía,” “Hojas de Lenguas Sueltas,” and “Decir la verdad.” In all, students worked with 74 first and early editions of histories, biographies, poetry, documents and periodicals from the sixteenth century to the twenty-first century. Each session included an assignment, culminating with a short, informal response to one of the books and the impact working with physical primary sources had on the student’s understanding of literary analysis.
Many thanks to the students who participated with such enthusiasm. We will always remember one early exclamation, “Best day of college ever!”
Muchos misterios están escondidos en la historia, from Cameron Dower

Entre los remedios q do fray Bartolome delas Casas…
Bartolomé de las Casas (1484-1566)
Fue impressa…en…Seuilla: en las casas de Jacome Croberger, Año de mill y quinientos cinquenta y dos años [1552]
F1411 C32
El 29 de marzo, tuvimos la oportunidad, como clase, a visitar a la colección de libros raros en la biblioteca Marriott. El poder tener en mano un libro publicado hace casi quinientos años es una experiencia extraordinaria. En esta ocasión analizamos libros del género de ensayo. La examinación del libro físico nos permite ir más allá en el análisis de la obra que simplemente leer el texto mismo. Yo me enfoqué en el libro del fray Bartolomé de las Casas. Bartolomé es una figura importantísima en la historia de la conquista de las Américas por España. Fue uno de las primeras voces para luchar contra el mal tratamiento de los indígenas por los conquistadores. En este libro, él expone sus razones por los cuales los indígenas merecen tener derechos sociales.
Esta copia del libro parece tener una historia muy particular. Al examinarlo, encuentro una inscripción en la segunda página detrás del título. La descifro como . ¿Quién fue este Alonso? ¿Cuándo vivió? La inscripción no nos dice, pero podemos encontrar algunas pistas acerca de la vida de Alonso. Como el libro fue escrito en una época en el cual pocos fueron letrados, Alonso probablemente tenía mucho dinero. También podemos ver que Alonso tenía un interés en la reforma social y la igualdad. Siguiendo el trabajo de investigación, encontramos la firma de Alonso debajo de la inscripción. Con la firma se encuentra un símbolo. Al seguir leyendo, vemos este símbolo en cada página derecha del libro hasta que termina después de la octava razón. ¿Por qué terminó de escribir el sello? Puede ser que se le acabó la tinta, o que perdió interés y dejó de leer, murió o cualquier otra razón. También vemos que debajo de la razón séptima, escribió de nuevo <razón séptima>. ¿Puede ser que la razón séptima fue el que le inspiró más o es que simplemente estaba practicando sus letras en el libro?
Muchos misterios están escondidos en la historia. La mayoría quizás no tienen respuesta. Sin embargo, sabemos que Alonso es un ejemplar de los que fueron afectados por los escritos de Bartolomé de las Casas.
A Connection to the Past, from Gardner Lange

Sixteen Century Mexican Broadside
Edwin H. Carpenter
Los Angeles: Dawson’s Book Shop, 1965
Z240.4 C37 1965
Giovanni Paoli was born near the turn of the sixteenth century in Northern Italy, but became known in Mexico as Juan Pablos, the founder of the first printing press in the Americas. Pablos ran the press until his death in 1563, at which time his son-in-law, Pedro Ocharte of France, took over its operation. Ocharte has garnered historical attention on account of his detention and torture at the hands of the Spanish Inquisition. Ocharte was labeled a heretic after allegedly printing a book that questioned the necessity of praying to saints. After lengthy court proceedings, he was acquitted of the charges and eventually allowed to resume printing, which he did until his death in 1592.
I encountered a 1560 print by Pablos and a 1587 print by Ocharte at The University of Utah’s Marriott Library in the Rare Books Department. Both are cartas de poder, or in English, power of attorney, documents. These broadsides may not initially be as thrilling as religious protestations that resulted in persecution and torture, but they captivated me for several reasons. First, I work part-time as a filing clerk for a law firm in downtown Salt Lake City. Nearly every day I read, copy, deliver and file documents that resemble these two broadsides. Handling these documents allowed me to form a connection to the past through experiences that I am familiar with as a legal clerk and aspiring attorney. Second, a close inspection of the documents and their details reveals historical insights that are sure to interest history enthusiasts.
The documents begin with the same phrase, which in English amounts to: Let it be known that the following individuals are witnesses to the authenticity of this document. This is followed in both documents by beautiful signatures of several individuals. Then the printed portion resumes, detailing what powers the client is agreeing to give to his or her attorney.
Interestingly, at the end of these sections, there is more handwritten cursive before the final signatures and notarization. This suggests that the broadsides were generic copies, which could be amended to the liking of the particular client by adding more legal wordage afterwards by hand. Being individual, double-sided sheets may also indicate that these were used for record keeping and not likely bound in books nor widely circulated. Fortunately for the scholars of our day, the publisher of this volume compiled information about many similar broadsides and in 1965 distributed several of them in copies of a book that details some of their history.
One of the most interesting differences I discovered between the two is the mention of slaves as assets in the 1560 carta de poder, which is not found in the 1587 version. Literary analysis textbooks are replete with encouragement to consider the historical context of the works being studied, and if we apply that principle here, it should cause any who examine these documents to consider what changed in the intervening decades regarding slave trade and issues of equality that would cause such a change to standard legal procedure.
A Universal Cultural Appreciation, from Annie Bonebrake

Refranes o proverbios en romance…
Fernando Núñez de Guzmán (ca. 16th cent.)
En Madrid: Por Iuan de la Cuesta, a costa de Miguel Martinez, 1619
PN6490 N8
Refranes o Proverbios en Romance is an encyclopedia of sayings and proverbs in Spanish, Italian, Austrian, Galician, French, Portuguese, Latin, and Greek. The book begins with a Spanish prologue written by Leon de Castrón, the “Maestro Leo.” The sayings are categorized alphabetically with their language of origin noted on the left side of each phrase in old Spanish. Some examples of proverbs documented in the book include “A cafas viejas, puertas nuevas,” in Spanish; “Boire iu fques a la lye-Frances,” in French; and “Comendo holgando, comendo trabalhando,” in Portuguese.
The physical qualities of this book contribute to an understanding of the text’s historical past. The outward appearance of Refranes o Proverbios en Romance is dilapidated, fragile, and used. The parchment cover of the book is creased and wrinkled, and has completely dissociated from the spine of the book. Gently lifting the detached cover from the spine reveals the book’s handmade string bindings. Finally, the text in the book was clearly produced with a printing press, as each individual letter was stamped into the book with visible force. All of these elements contribute to an awareness of a universal cultural appreciation for didactic proverbs and sayings since the book has survived over 300 years and has ultimately landed in the rare book department of a major university.
When considering objects spanning centuries of history, the object’s past must be analyzed in addition to the concrete characteristics of that object. Additionally, in order to conduct a literary analysis of a book able to withstand hundreds of years, one must consider what kind of abstract influence that book has had on a society to determine the author’s purpose for that work. For example, as I conducted a literary analysis of Refranes o Proverbios en Romance I first had to brainstorm for the reasons an encyclopedia of phrases and proverbs might be valuable to western European societies before I could begin to analyze any detailed text within the book; understanding an author’s purpose for writing the book is essential for fully comprehending a book’s literary worth. I determined that Refranes o Proverbios en Romance is an important work because it provides a reference for thousands of famous sayings across various cultures, which are valuable because they are tools used to convey morals or lessons.
My experience with Refranes o Proverbios en Romance allowed me to practice comprehension of an author’s purpose for a work in the greater context of a society or history. Because Guzman’s encyclopedia of phrases is more like a dictionary than a narrative with a plot, the process of literary analysis of this work was more abstract than concrete. In other words, an inferred understanding as to why a book of proverbs might be valuable to a society was more necessary for my literary analysis than the ability to interpret literary devices.
El arte didáctica, el arte para enseñar, from Olivia Blithell

El atlas abreviado, o compendiosa geografia, del…
Francisco de Aefferden (1653-1709)
En Amberes: A costa de Francisco Laso, mercader de libros, enfrente de S. Phelipe el Real de Madrid, año 1711
Fourth edition
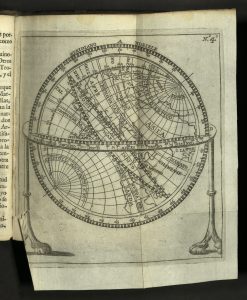
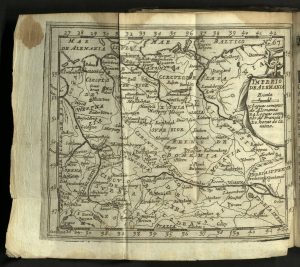
[This work] was published in 1711, two years after author Francisco de Aefferden (a Belgian cartographer) died, in Antwerp by a book merchant named Francisco Laso. It is a leather-bound pocket atlas containing descriptions of the world and very detailed, ornate maps that fold out. They depict bodies of water, rivers, forests, mountain ranges, common trails, and the names of places.
The maps for their time are extremely accurate, with distance scales and longitude and latitude indications on every map.
The pages crinkle when you turn them and you can smell the leather of the binding as you read the book. The reader can see the years in the leather — the binding is wearing thin. You can take a trip around the world, your mind can visit anywhere.
The reader can learn about “El Mundo Nuevo,”
then see all of the forests and mountains in “Alemania” — a glimpse into the past world.
We can see the signatures and notes of previous owners. The waves of their cursive from ink and quill contrast with the Old English-styled font of text. This little pocket atlas was their only tool to get from point “a” to point “b,” when traveling in strange and foreign lands. In today’s world, our pocket atlas is our iPhone, a pocket-sized computer. We have the world in our hands, a technology unimaginable in 1711.
We can see how the world has evolved since the 17th century, both physically and intellectually. There are large cities where forests used to be, some of the towns have changed their names, but many remain. Even though our world has changed, the past is still with us.
We can read the words in the text and see how the people of the day thought. The Spanish text is very beautiful, like Shakespeare. It is different from how today’s Spanish is spoken. It is more poetic and meant to teach, el arte didáctica, el arte para enseñar.
Es Algo Incredible, from James Smith

Reales ordenanzas para la dirección, régimen y gobierno del importante cuerpo de la minería de Nueva-España, y de su real tribunal general. De orden de su majestad
Madrid, 1783
First edition
KC729.5 M48 1783
Como sugiere su titulo, este el libro era hecho con el propósito de ayudar el país de España ministrar sus minerías. Para entender este libro es necesario que primero entendemos porque la industria minería era tan importante por España durante el 18º siglo. La minería de plata pagaba mucho y por eso los indignos de España estaban muy interesado de minarlo. Por la potencia que la minería tenia durante esta época Nueva-España dependía mucho en la minería y por eso creía este libro para introducir reglas de cómo la minería debería funcionar.
Es algo incredíble a pensar que este libro que era publicado en 1783 ha durado por mas que 200 años con las mismas paginas, tinta, y encuadernación. No hay muchas cosas que pueden perdurar por siglos, especialmente los libros. Pero el hecho de que este libro todavía esta en buena condición lleva un mensaje y entendimiento de la importancia de este libro sin abrirlo.
El libro tiene mas que 200 paginas que son separadas por “títulos” que parecen como capítulos. No era escrito por mano pero imprimió con maquina que es algo interesante porque era muy caro a imprimir. Este también refleja que el libro llevaba mucha importancia. Sin leer la primera pagina el lector puede saber que este libro no era hecho con el propósito de entretener, pero algo muy serio.
Si vemos la pagina 23, titulo II, dice “jueces de minas lo serán las respectivas justicias reales, conforme a las leyes de la recopilación de indas, en todo lo que por estas Ordenanzas no se cometiere a las diputaciones del cuerpo de minería.” Aunque Nueva-España era una monarquía usaban jueces y otros formes de gobierno. Si leemos esta articulo parece como una oración aburrida respecto a un tipo de trabajo. Pero realmente este articulo, junto con el resto del libro, contiene muchísima historia.
Para entender la verdadero sentido de esta oración es necesario que primero entendemos los políticos de España, la economía, y la importancia que la minería tenia en la país.
Another Level of Depth, from Owen Orchard

Diario de Mexico
Mexico City: Oficina de Don Mariano Jose de Zuniga y Ontiveros, 1805-1817
AP63 D5
We as a class were given the opportunity to visit the Marriott Library’s rare book collections where we could analyze and observe amazing works of Spanish literature dating back to the 15th and 16th centuries.
The piece that I gravitated towards most was Diario de Mexico. This journal began publication in 1805 and was the first daily news periodical in Mexico. It discussed philosophical, moral, and artistic issues, such as the function of theater. The articles were written by a diverse collection of authors, adding depth to the conversations.
The physical condition and layout of the periodical is impressive. The Rare Books set is bound in a leather cover of a date later than the publication, very much intact. The issues themselves have almost no tears or stains.
Each issue begins with a poem. Many of the articles go into great depth in ways perhaps unexpected by the 21st century reader and perhaps even in the 21st century. Examples include, “Cosas que incomodan en Mexico” and “Falibilidad del la Medicina.”
The opportunity to view and actually touch these works is incredible. When you feel and turn the pages of these books its a totally different experience than just hearing about them. You are able to see whether or not a book was printed or handwritten and also what material the book was made from. This adds so much to one’s literary analysis because you can make guesses as to why it was written on that material or why it was written in that way based off of the time period it came from.
All in all, being able to interact with these pieces in person added another level of depth to my analysis. By looking and touching, I discovered that these texts contain centuries of knowledge and insight as well as an infinite number of underlying details. I have very much enjoyed my time with the rare book collections and now have a vastly greater understanding and interest in this type of study.
The Need to Spread Word, from Anna Paseman

Colección de documentos relativos al departamento de Californias publicados por el ciudadano Manuel Castañares
Mexico: Imprenta de la Voz de Pueblo, 1845
As its title suggests, the text Colección de documentos relativos al departamento de Californias publicados por el ciudadano Manuel Castañares consists of a compilation of letters, speeches, and essays written by Manuel Castañares. Castañares served as one of California’s represetatives to Mexico’s National Congress during the mid-1840s, and his compositions touch on a number of important historical and literary subjects. The physical text itself, a thin, fragile, paper pamphlet, one of only 11 known to exist, exhibits its own literary significance.
Among the text’s central themes are descriptions of various aspects of the California territory, including its indigenous population, Spanish missions, ports, agricultural sectors, and the 1843 discovery of gold. The mention of the discovery of gold is particularly important because this text is believed to be the first pamphlet to document the discovery and mining of gold in California.
While the documentation of the discovery is interesting, Castañares’s relevant commentary is of greater interest. In various letters, he repeatedly voices concern that the Mexican federal government must proactively safeguard California, such that a foreign power does not take interest in, and devastate, its precious resources.
Castañares’s concerns regarding California’s abundant resources extends to his broader discussion of foreign intrusion into the territory, and the failure of the Mexican government to sufficiently attend to its security needs. Describing the daunting threat posed by the United States, in particular, Castañares writes, “El estado que hoy guarda la república, las tendencias y conatos de una nación vecina para continuar usurpando nuestro territorio, el carácter de invasión que manifiesta toda la prensa americana y nuestra inercia, me hacen temblar por la suerte de la república, si no se atienden nuestras fronteras, principalmente mi Departamento.”
The concern that Castañares expresses for unrest in California in 1845, and the assertive nature of the American government on its frontiers, is foreboding; the next year, 1846, California experienced the uprising known as the Bear Flag Revolt. The Mexican-American War followed, lasting from 1846-1848, and by early 1847 California officially came into the possession of the United States. In this sense, Castañares’s writings serve as a valuable tool for understanding the events leading up to the transfer of California from Mexican to American hands.
The relatively small and cheaply produced nature of the pamphlet likely indicates that it was meant to be portable and read by many. While it is difficult to know with certainty Castañares’s intention in publishing his writings, it is apparent that he felt the need to spread word of what he perceived as a threat, and perhaps, to raise concern among others such that the issue of foreign intrusion would gain attention, and the Mexican government would respond sufficiently. By handling the text, and accepting Castañares’s intentions as previously described, it is easy to imagine the serious political conversations that must have been happening in California during the 1840s, and the types of information that would have informed Mexicans on the state of the territory. Moreover, the text serves as an interesting reminder that California was not always a part of the United States, and that the history of American expansion is not necessarily one of peaceful acquisition.
Somewhere, At Some Time, Someone, from Carlos Ixta
 [
[
Tratado de Paz, Amistad, limites y, arreglo
Mexico: Impr. De I. Cumplido, 1848
Second printing
E408 M62 1848

Treaty of peace, friendship, limits, and settlement between the United States of America and the Mexican Republic: concluded at Guadalupe Hidalgo, February 2, and ratified, with the amendments, by the American Senate, March 10, also ratified by the Mexican Congress, May 25, 1848
Washington, 1848
E408 U583
The Spanish version of this text was printed months after the English edition of the text. I had the opportunity to be able to look at both of them and to compare and contrast the two. The history of these texts is very powerful to me. As a Mexican-American, I have always had a special interest in the events surrounding the American colonization of the U. S., as well as the Mexican-American war, and other historical events. Seeing, reading, and holding the texts in the rare books collection was a profound experience for me. I imagine being back in such a time, perhaps living in California — or even Utah for that matter — both of which were Mexican territories at one time. Then, after years of war, and thousands of deaths, to receive a really small book, perhaps not even suitable to be called a book, somewhat of a 2-page decree from either the Mexican Republic or the United States government stating that the land I’ve lived on my whole life suddenly belongs to a whole different government. How peculiar that must be! Many people had a hard time believing what had just happened and for this reason the Mexican government printed an edition of the peace treaty with an added forward which basically stated that it was true, that this is really happening, and the people must accept it.
As I sat there imagining what it must have been like or how strange an experience that is, it only added to the feeling to be able to hold physical copies of a books such as these. I realized, that these are originals, that somewhere, at some time, someone had helf up the exact copy that I was able to hold and that this really happened to them. Overall, it was an honorable experience to see these and many other books like these at university. There is definitely a difference in reading about the history of things like this in high school history class and being able to hold the actual books published at the time being studied.
Same Event, Two Different Books, Two Different Ways, from Dylan Slavens

Tratado de Paz, Amistad, limites y, arreglo
Mexico: Impr. De I. Cumplido, 1848
E408 M62 1848

Treaty of peace, Friendship, limits, and settlement between the United States of America and the Mexican Republic: Concluded at Guadalupe Hildalgo, February 2, and ratified with the amendments, by the American Senate, March 10, also ratified by the Mexican Congress, May 25, 1848
Washington, 1848
E408 U55 1848
I had the opportunity to hold in my hands these two books during my visit to the Rare Books Department in The University of Utah’s Marriott Library. Although these two books were printed examples of The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo between the U.S. and Mexican governments, I observed many differences between the two. One of these books was written and published in Mexico while the other was written and published in the U.S.
One of the first differences I noticed about the two books was that the physical quality and appearance of the one printed in the U.S. was a lot better than the one from Mexico. The cover and the paper of the U.S. copy were all in a lot better condition. The Mexican copy seemed to be falling apart and the physical materials used to make the book seemed to be cheaper. The U.S. copy had many more pages than the one from Mexico, which surprised me because the Mexican version had both the Spanish and English translations on both sides of the pages.
Having physical contact with these two books helped me process and analyze the differences between the two much more easily. The U.S. copy was written more like a dialog and a journal while the Mexican copy seemed to be more straightforward and official.
The book from Mexico officially explained the protocols necessary for the conclusion of the treaty, including the amendments made to the treaty by the United States. In my short 45 minutes of analyzing and observing these two books I can see many differences not only physically but also literally between the two. Same event, two different books, two different ways of writing and presenting the information of what happened. It was such a unique experience of actually having and holding the two books in my hands.
Revealing Something A Glowing Wall of Text Never Could, from Marc Jackson

Gobierno general: Ministerio de justicia
Benito Juarez (1806-1872)
Chihuahua: 1859
KG3035 A5 1859
The newspaper article is gently held in place by a protective sleeve. Frayed edges and discoloration characterize its tattered face. When turning the pages it almost seems like they could split in two if one was careless. The irony is that this article’s pages were never meant to be turned carefully. The thin paper and poor condition reveal something a glowing wall of text never could. They reveal that this article was not written for royalty, politicians, or clergy but for the masses. The Mexican government printed this newspaper cheaply so it could be sent to as many people as possible. Knowing that the author, Benito Juarez, wrote Gobierno general for the public opens up a deeper analysis. Instead of simply setting up new laws concerning marriage, the purpose of the text becomes gaining public support for dramatic social changes. Instead of the verse-like statements representing legal language, they can represent scripture and therefore the fight Juarez pushed to lower the influence of the Catholic Church on the government. In other words, the purpose of the article is to incite social change and the theme is the replacement of Catholic doctrine with democratic law.
Without feeling the thin pages and physically interacting with the original work it would be much harder to conclude that the audience is the general public. If the reader only had the words themselves it’s likely they would conclude that Juarez only wrote it for lawyers. However, touching the original page transports the reader to 1859. A lawyer doesn’t hand over the newspaper, an excited Indian does. He talks about how much it means to him that an indigenous Mexican is representing him and that the government is openly talking about issues that until recently were taboo. This newspaper article proves that information essential to understanding literature is hidden everywhere the words aren’t, preserving words isn’t enough, the physical objects and their connection to the past must be preserved or our understanding of older texts might never dive beneath the surface.
Bound Together in Honor of Its Memory, from Marisol Padilla Fragosso

Madrid Comico
Madrid, 1885-1897?
AP111 M347
The book that caught my eye on my third visit to the Rare Books section of the Marriott Library, or as I and several of my classmates have called it, the “Restricted Area,” was Madrid Comico, “Comical Madrid” in English, a Spanish magazine published between 1880 and 1923. This magazine contained anti-Modernism propaganda and was full of humorous stories and comics, as the title implies. The issues in Rare Books have been bound together in what appears to be a binding contemporary to the time period of the magazine’s run. At some point, the owner of these issues had them bound together, giving the sense of a commemorative book. Who did this and why they did so is not known, however, it would be appropriate to guess that this book came to be because the magazine shut down in 1923, as if the issues were bound together in honor of its memory.
From all of my experiences and interactions in the Rare Books area, I have learned to appreciate books even more than I did before. Some of these books are centuries old and are in incredible condition, which is great for the reader because this means the text is legible instead of smudged, pages contain no significant rips or tears (if any), and no pages appear to be missing. This is important to the reader’s experience. There is no gap in the flow of the text, due to illegibility, a condition that might ruin the world of the reader and what the author had in mind.
When you touch a book that is over a hundred years old, you can’t help but feel awestruck and humbled; of course, precautionary measures are taken so that the oils in human skin don’t harm the books (that’s what the baby wipes are for) and you have to be gentle with the binding — opening, closing, and flipping through the pages gingerly. Another thing that I realized from my experience with these rare books, is that books truly are precious treasures: If they were not to be treasured, someone would not have taken the time to carefully preserve them in the best condition possible.
While holding these amazing books, I couldn’t help but apply textual analytic tools that I learned in my textbook for my Spanish class, Aproximaciones al estudio de la literatura hispánica, 6ª ed. The main tool that I used was looking at the Who, Where, When, Why, and How. Once you are able to answer these questions about a book, you are better able to understand the depth of the text and the author’s, as well as the publisher’s, vision for it. When I apply this tool to my analysis of texts, I feel as though I am tapping into the mind of the author and publisher, almost as if I was a profiler looking at a crime scene, figuring out who did it, when they did it, how it was done, and the motive behind the crime.
A Personality Distinct From All Others, from Tosh Noskowski

Siluetas: con retratos y…
Urbano Gonzalez Serrano (1848-1904)
Madrid: R. Serra, 1899
PQ6072 G6
Urbano Gonzalez Serrano was a literary critic as well as philosopher and professor. Siluetas is a compilation of brief biographies about various authors of his time.
Each biography begins with a picture of each author and a copy of something handwritten by him that includes a signature.
The book, in and of itself, is really small — it can fit in the palm of your hand. This makes is very approachable, as many large books can be intimidating and bring a sense of prestige with them. A small book makes the literary analysis easier because it does not give the impression of being above reproach.
Literary analysis can be augmented by being in physical contact with the book because it brings to light how the book was meant to be read, and can even help identify target audiences for the text. The size and weight of it may limit those who were meant to read it, which can be a key factor when analyzing aspects of a text.
The literary analysis tools focus on trying to understand the meaning and purpose of any given text. It can be approached via different questions and angles depending on the genre of the text, but seeing the books in person truly gives weight to these questions. It’s not just a bunch of words in a textbook any more, it gives purpose to what the literary analysis is trying to do. Simply analyzing a text on a screen or in a textbook doesn’t represent the work as it was meant to be. The physical form, age, and wear and tear of a work gives it a personality distinct from all others. From here, the analytic tools learned through a textbook can be applied in a much more meaningful way.
The Search for Truth, from Camille Morgenstern

González Videla, el laval de la America Latina: Breve biografía de un traidor
Mexico City, 1949
First edition
F3099 G6 N4
When perusing the rare texts around the themes of “ensayo” and “decir la verdad,” i.e. the search for truth, this folleto by Pablo Neruda caught my eye because of the interesting and rich historical context surrounding the piece, but also because of Neruda’s specific use of the book as a medium for disseminating his truth.
The folleto is presented as a collection of brief pieces in a wide range of genres, from poems to essays to letters to testimonies, all denouncing Gabriel González Videla. Neruda was, at the time, a Communist Party senator and member of the Communist Party of Chile. Videla was a presidential candidate representing the Radical Party and asked Neruda to be his campaign manager. Once in office, Videla turned against the Communist Party, violently repressing a Communist-led miner’s strike. Neruda disassociated from Videla, and began to publicly critique him in speeches, which carried over into the form of the folleto. In this text, Neruda compares González to Pierre Laval, prime minister of collaborationist France during German occupation in WWII.
What fascinated me most was Neruda’s use of the physical book to convey his truth. The book itself is very small and lightweight, facilitating the circulation and distribution of the text. The cover art, by renowned Spanish (and Communist) muralist Josep Renau, is strikingly bold, and is the only color found throughout the book. His use of strong imagery here mirrors the forceful tone of the texts inside, and his use of other images such as posters and photographs to supplement the vignettes strengthens his story and allows the book to reach a wider audience as well. The folleto contains a number of different essays in forms such as denouncements, poems, records, and more, with titles such as “El Complice de los Nazis,” “Violader de Convenios Internacionales,” and “El Traidor Contra su Pueblo,” presented together in a format resembling a newspaper. This method enhances the underlying argument that Neruda’s experiences are truth, and breaks the truth down into simple yet poignant terms.
Interacting with the physical form of the book was a much richer form of literary analysis because it provided another layer of understanding. By holding the form in which the text was intended to be absorbed, I was able to connect the text itself to the physical format and understand more clearly Neruda’s intentions behind creating the folleto in the way he did. Additionally, it connected me more closely to the historical context in general, because I was in contact with a tangible object from that time.
I Will Be Coming Back, from Cameron Dower

Excavator, Barcelona, Excavador
Jake Tilson (b. 1958)
London: Woolley Dale, 1986
During the time I had the opportunity to visit the Rare Books Department at the J. Willard Marriott Library at the University of Utah, I found some amazing books. One that really reached out to me was Excavator, Barcelona, Ecavador. This book has photographs and text. It was made from a clandestine pro-terrorist publication on police detecting methods. The chapters are as follows: 1-1 Burial attempt. 1-2 Immortal Man. 2-1 Horizontal Clock, Barrio Gatico. 2-2 Department of Correction. 3-1 How to Film a Panic. 3-2 Making Impressions Visible Again. 4-1 The Killing Jar. Thought provoking, no? Just the titles themselves make you want to take a second glance.
The cover has aspects of the world, people, secrets and color you would not normally find in modern day art, or in classical art.
Each picture contains answers to questions you want to ask. Slices of humans, places, world politics and personal views are riddled into the art. Tilson uses maps and locations in sections. The style seems almost crude. It has a very rough yet very thought-out look. It feels as if you could look at only one part of the painting and feel enraptured.
The text is in the art itself. It is rarely in a paragraph. Tilson adds poetry in and around the vivid yet vague images. This invokes an uneasiness in the reader. In only short verses Tilson alludes to politics, science, government and controversial social topics. As the reader turns the page, he fears that he will miss something important in each corner of the painting. Tilson uses symbols. The reader may see them in each of the photographic works. This reader found symbols of government, Egypt, cartography, cities, numbers, dials, clocks, measurements, footprints, fingerprints, hidden societies, and landmarks, all seeming to mean completely different things within the art. Within each piece and as a collection, there is tension and the suspicion that all have aspects in common, yet part of a puzzle — we don’t see the big picture…yet.
This was a fantastic experience and I would recommend it to anyone who has an interest in the rare, the historical and the bizarre, an experience not the same as we have every day from mainstream media. Thank you. I will be coming back.
*Editor’s note: minimal changes of one form or another have been made to each of these short essays, reflecting a few minor corrections in spelling and punctuation, or in slight clarification of the text, or in reducing the text to fit the blog format.


















































You must be logged in to post a comment.